Climate Risk Assessment of Small and Medium Hydropower Projects in Southeast Europe, Turkey, the Caucasus and Morocco
The objective of this assessment is to identify and assess the climate risks associated with small and medium hydropower projects in selected regions.
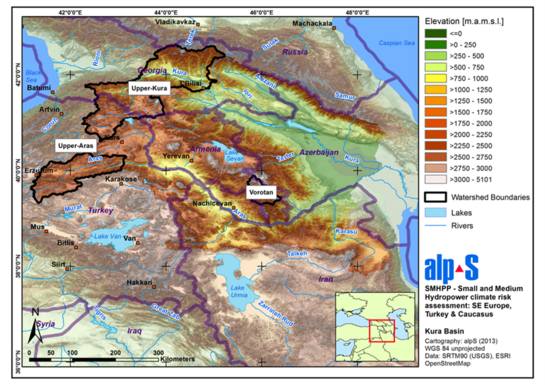
Hydrology is a key determinant of the annual energy yield of hydroelectric power plants (HPPs), and as hydrology is highly variable, it poses a risk to such investments. In turn, hydrology is highly sensitive to climatic conditions and, consequently, to climate change. Small and medium-sized HPPs are particularly exposed to climate risks, i.e. climate change and climate variability.
The study aims to better understand the impact of these factors on small/medium hydropower plants, the risk involved in such investments, and the degree and nature of uncertainty and its impact on banks' project finance and decision making. The study carries out an analysis of such risks in Southeast Europe, Turkey, the Caucasus and Morocco using a river basin approach for a number of selected major river basins.
- Compile climate data, conduct regional review of historical climate change impacts
- Select key river basins based on specific criteria and case studies
- Assess potential for changes in water availability, impact of climate change on competing water uses
- Analyse how hydropower financial performance may be affected by climate variability and change
- Recommend decision-making criteria for the financial performance of hydropower investments
- Advise on necessary adaptation of environmental and social action plans
- Recommend methodology for future assessment of hydropower projects
